“What makes you stand out from the crowd?”
Were you ever stepped out in an interview by someone you though has less impressive resume or lower qualifications? The reason may be that they excelled in the so called soft skills. Namely, one of the main goals of any university program, is to ensure that the skills educated in the classroom are applicable to post-graduate employment; but, with the evolution of educational trends, the versatility of studies, the availability of masses of qualified personnel etc, it’s getting tougher and tougher to get a permanent job.
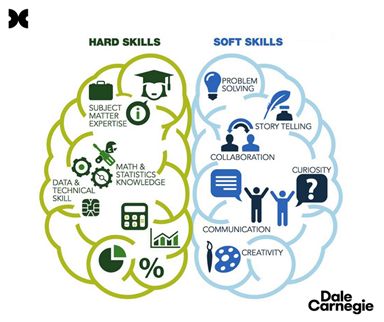
To gain an advantage over competitors, students have no choice, but to add value to their technical skills with soft skills to show their true potential. Technical skills are academic skills, experience and level of expertise, while soft skills are self-developed, interactive, communication, human and transferable skills.
Today, most employers want to hire and promote people who are reliable, resourceful, ethical, self-directed, effective communicators, willing to work and learn, and have a positive attitude.
Hard skills vs soft skills
Every useful skill is a life skill. A skill refers to the level of individual performance or ability to perform a particular task (Noe, Hollenbeck & Gerhart, 2015). Some skills may be more or less relevant depending on the individual’s life circumstances, culture, beliefs, age and location. The technical element measures “hard” technical skills, while communication elements measure “soft skills” including attitudes and approaches (Patacsil & Tablatin, 2017).
Hard skills, as defined by Rainsbury et al., (2002), are skills related to the technical aspects of performing multiple tasks on the job. Technical skills or hard skills generally refer to the knowledge and skills that help employees perform their jobs effectively, and these skills are used to identify job candidates on paper. Those skills must haven by workers to start lessons, lead classes, set up group discussions, organize classrooms, and write in good way (Sopa et al., 2020).
Soft or life skills are the personal qualities that help employees advance in the workplace. Life skills include many areas including leadership, conflict management, communication skills, creativity, critical thinking, problem solving and decision making, the ability to collaborate, and interpersonal skills that contribute to good citizenship. Further, soft skills are the accumulation of personal qualities, attitudes and social etiquette that make someone unique. They are important for professional development, intellectual property rights maintenance and effective communication. There are many important soft skill to use in the workplace. Therefore, soft skill training for young people especially should start when they are students perform efficiently both in the academic environment and in the future workplace (Vasanthakumari, 2019). The presence of both hard and soft skills together is necessary for all employees to be successful in their job roles (Sopa et al., 2020).
https://www.facebook.com/Dalecarnegie.Tunisia/photos/a.511170035616430/2457129597687121/
Research findings on the importance of soft skills in the workplace
According to a survey by the Stanford Institute and the Carnegie Mellon Foundation, soft skill acquisition accounts for 75% of long-term professional success and technical skills account for only 25% (Vasanthakumari, 2019).
Ross School of Business at Boston University and the University of Michigan did research about workers with soft skills, and workers without soft skills. Results showed that works with soft skills are 12% more productive than those without these skills (Vasanthakumari, 2019).
A report from Harvard University indicates that 85% of workplace successes are due to soft skills and only 15% are due to technical skills (workforce.com).
A public survey conducted by McDonald’s in the United Kingdom predicts that by 2020, more than 500,000 people will be locked out of the labor market due to lack of soft skills (Vasanthakumari, 2019).
Why soft skills are so important?
In light of the complex environment we live in today, which is characterized by rapid changes and daily challenges, a question arises: Are we equipping the next generation – children and youth – with the appropriate life skills to adapt to the world around them?
Besides, working with young people needs the growth of these young people and the process they experience. Now that digital technology is a priority, young people are having less and less live communication. Despite being very familiar with the internet, they often lack the ability to talk face-to-face.
The changing nature of this digital age must be met with a renewed, inclusive, and continuous vision of education. Therefore, teaching and learning life skills – also called twenty-first century skills – is critical to enabling children and young people to achieve success in education, employment, and personal goals. However, few educational systems have integrated life skills into their educational curricula. One reason for this is challenges related to the lack of knowledge about how to measure and evaluate life skills ((John, 2010).
Building on the Regional Framework for Life Skills and Citizenship Education in the Middle East and North Africa, UNICEF and the World Bank have developed the Life Skills and Citizenship Measurement Tool. The tool was launched in 2017 to better equip children and youth to produce knowledge and to address the transitions from childhood to adulthood, from education to work, and from the ill-advised development of responsible and active citizenship. Over the past three years, the Life Skills and Citizenship Education Tool has been developed in order to inform ministries of education about a vision of a credible national system that will bring them closer to grade 7 students’ grades, based on the eight life skills, and to identify subgroups of students who need more support (https://www.unicef.org/mena/ar/).
The application of the life skills and citizenship education tool has several advantages or objectives, the most important being:
- Improving life outcomes through educational policies and targeted interventions that need to understand and distribute life skills outcomes to school students.
- Integrating life skills into national education systems and targeted interventions through the content of teaching and the teaching and learning process requires consistency with life skills outcomes.
- Monitoring life skills acquisition, and hence the effectiveness of learning policies and targeted interventions, requires regular assessment of life skills outcomes and trends over time. (https://www.unicef.org/mena/ar/).
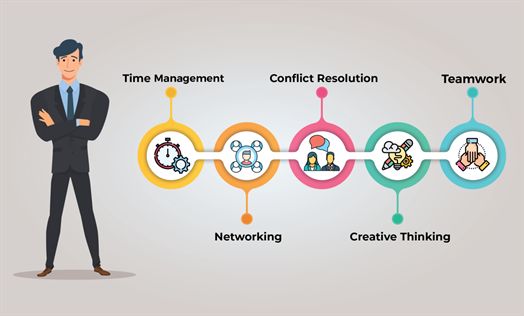
Fig 2. Soft Skills in the Workplace are in demand
https://thetalentgames.com/soft-skills-in-the-workplace-all-you-need-to-know/
How to improve your soft skills?
According to Schulz (2008), there are two ways to improve your soft skills. First, by enrolling in formal training, taking courses on language, presentation skills, conflict or cultural management. This is a proven concept that has the advantage of having some kind of certificate at the end of the course and is useful when applying for a job. Second, the acquisition of other sort of soft skills is usually self-training based on books. It is true that changing an individual’s characteristics requires a long-term practice. Therefore, Schultz concludes, self-training may be more helpful in improving this. Other authors showed that by providing soft skill training, management institutions can raise student employability to a much higher level (John, 2010).
The Canadian academic Benoit Chalifoux, said: if the soft skills are essential, you must daily leave your comfort zone to develop them. To achieve this, he proposes a three-step approach.
- Do a self-diagnosis by asking yourself this series of questions: which require honest answers: How do you see yourself? What are your values? How do you relate to others? What do you believe in? Identify three of your strengths and then three of your weaknesses.
- Get out of your comfort zone. Easy to say! “Most people don’t like adversity. By forcing yourself to face it, to get out of your routine, business opportunities will multiply. In fact, what you perceive as a discomfort zone should be your comfort zone. Be disciplined and make it your new routine, and you’ll never stop learning.»
- Be selfless. Empathy and a sense of community are two sine qua non conditions for your career progression. “Stop talking about yourself and worry about others, without expecting anything in return,” asserts Chalifoux. Celebrate their success. The happiness of others should concern you more than your own.»
Conclusion
Soft skills and training methods appear to play an important role in the process of searching or applying for job opportunities, as well as in employee performance in the workplace. While hard skills contribute to the successful completion of tasks related to a particular job, soft skills are essential to creating a positive atmosphere in the work environment that helps raise productivity and achieve the company’s goals and vision. In summarizing, job performance was predicted by soft skills and applied training methodologies. Training methodologies can be expected to affect the transfer of soft skills acquired during training to the workplace, which inevitably improves job performance.
According to experts, training in a person’s soft skills begins as a student and extends to the technical skills required at the manager’s entry level. It is his soft and conceptual skills that help him reach the heights of his career. Therefore, this article sheds light on soft skills training program as part of the management curriculum. So, think about improving your technical and soft skills to get the right job for you, and make sure to make it clear and mention it well in your resume and during the job interview.
References
- Azim, S., Gale, A., Lawlor‐Wright, T., Kirkham, R., Khan, A., & Alam, M. (2010). The importance of soft skills in complex projects. International Journal of Managing Projects in Business, 3(3), 387– 401.
- John.J (2010). Study on the Nature of Impact of Soft Skills Training Programme on the Soft Skills Development of Management Students. Pacific Business Review, pp. 19-27
- Noe, R.A., Hollenbeck, J.R., & Gerhart, B. (2015). Fundamental of Human Resource Management. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Patacsil. F.f , tablatin. C.ls (2017). Exploring the importance of soft and hard skills as perceived by it internship students and industry: a gap analysis. Journal of technology and science education jotse, 2017 – 7(3): 347-368 – online issn: 2013-6374 – print issn: 2014-5349
- Rainsbury, E., Hodges, D., Burchell, N. & Lay, M. C. (2002). Ranking workplace competencies: Student and graduate perceptions. Asia-Pacific Journal of Cooperative Education, 3(2), 8-18. https://hdl.handle.net/10289/3219
- Schulz.B (2008). The Importance of Soft Skills: Education beyond academic knowledge. Journal of Language and Communication. Pp 146-154.
- Sopa. C. A , Asbari.M , Purwanto. A , Santoso. P. B , Mustofa , Hutagalung.D , Maesaroh.S , Ramdan.M, Primahendra.R (2020). Hard Skills versus Soft Skills: Which are More Important for Indonesian Employees Innovation. International Journal of Control and Automation Vol. 13, No. 2, pp. 156 – 175
- Sousa, M. J., & Rocha, Á. (2019). Strategic Knowledge Management in the Digital Age. Journal of Business Research, 94, 223–226. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.10.016
- Vasanthakumari.S (2019). Soft skills and its application in work place. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews e-ISSN: 2581-9615, Cross Ref DOI: 10.30574/wjarr
- https://harappa.education/harappa-diaries/what-are-life-skills-and-how-to-improve-them/
- www.workforce.com
- https://www.unicef.org/mena/ar/تعليم-المهارات-الحياتية-نحو-رؤية-تجديدية-للتعليم/قصص
- https://www.cpacanada.ca/fr/nouvelles/travail/2018-12-06-developper-competences-generales